Key words: dengue fever, global, threat, fight, virus, mosquito, infection, prevention, treatment, diet
Dengue fever is a serious disease caused by a virus that is transmitted by mosquitoes. It can cause high fever, severe headache, muscle and joint pain, bleeding, and shock. It can also be fatal in some cases. Here is a comprehensive note on dengue fever, its cycle duration, pattern, preventive measures and treatment along with dietary support to treat this.
Cycle duration:
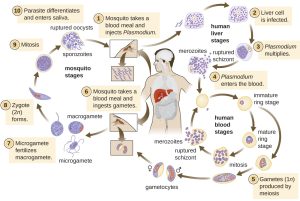
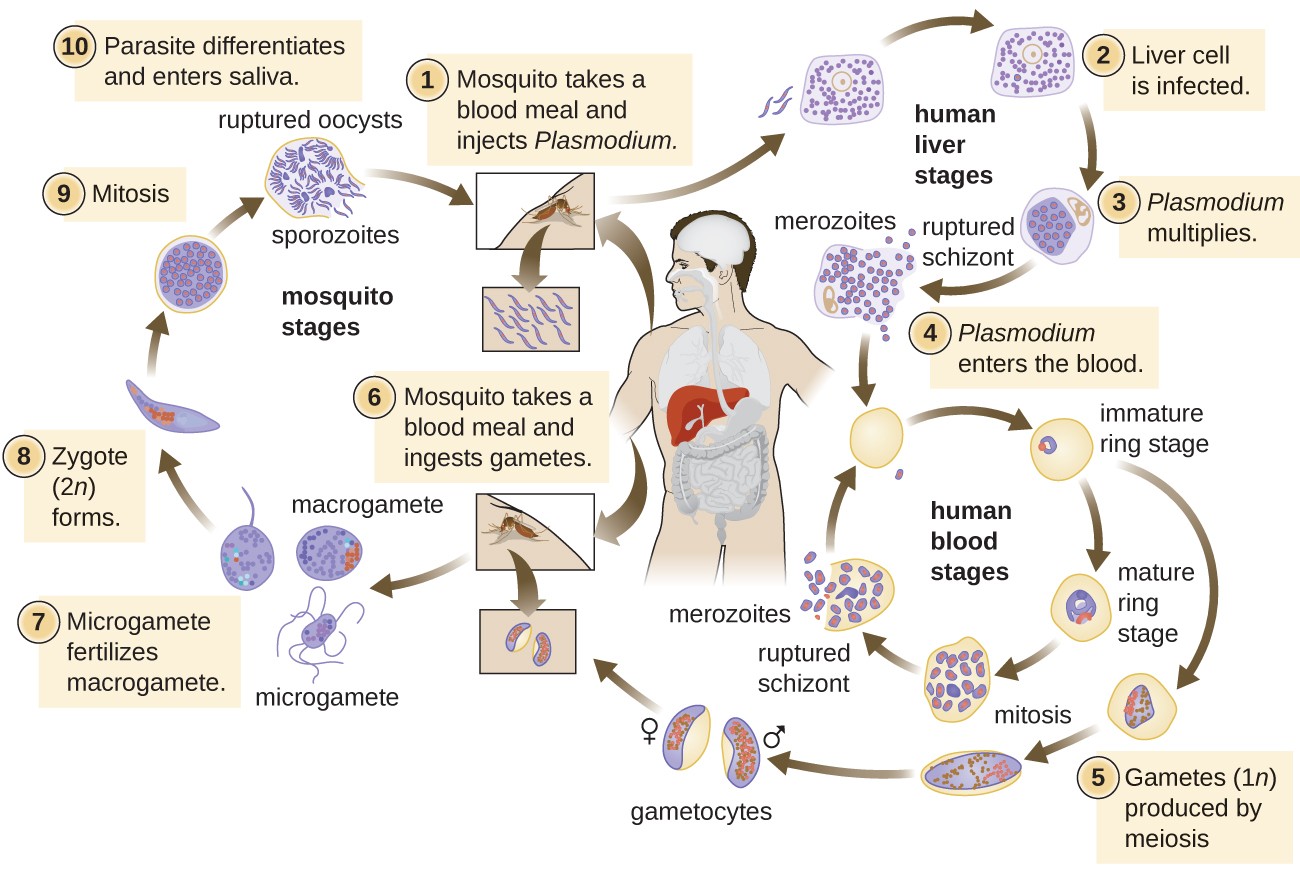
The cycle of dengue fever involves two hosts: humans and mosquitoes. The virus is transmitted from an infected human to a mosquito when the mosquito bites the human. The mosquito then becomes infected and can transmit the virus to another human when it bites again. The virus can also be transmitted through blood transfusion or organ donation from an infected person. The incubation period of the virus in humans is 4 to 10 days, meaning that the symptoms usually appear within this time after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The symptoms of dengue fever typically last for 2 to 7 days, and most people recover after about a week. However, some people may develop severe dengue, which can cause life-threatening complications within a few hours after the fever goes away12.
Pattern: Dengue fever has four distinct phases: febrile, critical, recovery, and convalescence. The febrile phase is characterized by a sudden onset of high fever (104 F or 40 C), headache, pain behind the eyes, muscle and joint pain, nausea, vomiting, rash, and swollen glands. This phase lasts for 2 to 4 days. The critical phase occurs when the fever subsides and the blood vessels become leaky and damaged. This can lead to bleeding, shock, organ failure, and death. This phase lasts for 24 to 48 hours and requires immediate medical attention. The recovery phase begins when the blood pressure stabilizes and the bleeding stops. The patient may still have fluid accumulation in the body and may need supportive care. This phase lasts for 2 to 3 days. The convalescence phase is the final stage of recovery, when the patient regains strength and appetite. This phase may last for a week or more12.
Preventive measures:

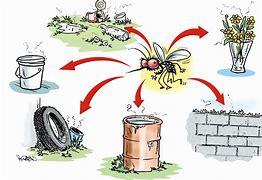
There is no specific vaccine or medicine to prevent dengue fever. The best way to prevent infection is to avoid being bitten by mosquitoes and to reduce the mosquito population. Some of the preventive measures are:
- Use insect repellents on exposed skin and clothing. Choose repellents that contain DEET, picaridin, IR3535, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, socks, and shoes when outdoors. Avoid dark-colored clothing, as it attracts mosquitoes.
- Use mosquito nets, screens, or air conditioning to keep mosquitoes out of your home. Repair any holes or gaps in the walls or windows.
- Eliminate mosquito breeding sites around your home. Drain any standing water in containers, pots, tires, or buckets. Change the water in vases, birdbaths, or fountains regularly. Cover water storage tanks or barrels with lids or mesh.
- Avoid traveling to areas where dengue fever is common, especially during the rainy season. If you do travel, follow the above precautions and consult your doctor before and after your trip123.
Treatment: There is no specific medicine to treat dengue fever. The treatment is mainly supportive and depends on the severity of the infection. Some of the treatment options are:
- For mild symptoms, rest as much as possible, drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated, and take acetaminophen (paracetamol) to control fever and relieve pain. Do not take aspirin or ibuprofen, as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
- For severe symptoms, seek immediate medical attention at a clinic or hospital. You may need intravenous fluids, blood transfusion, oxygen therapy, or intensive care to manage the complications of dengue fever.
- For pregnant women, infants, or people who have had dengue fever before, be extra cautious and monitor your symptoms closely. You are at higher risk of developing severe dengue and may need special care123.
Dietary support: A balanced and nutritious diet can help your body fight the infection and recover faster. Some of the dietary tips for dengue fever are:
- Eat foods that are easy to digest, such as soups, porridge, boiled vegetables, fruits, yogurt, and eggs. Avoid spicy, oily, or fried foods, as they can irritate your stomach and cause nausea or vomiting.
- Eat foods that are rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, strawberries, guava, kiwi, and papaya. Vitamin C can boost your immune system and help your body heal the damaged tissues.
- Eat foods that are rich in fluids, such as water, coconut water, fruit juices, herbal teas, and soups. Fluids can help you stay hydrated and prevent dehydration, which can worsen the symptoms of dengue fever.
- Eat foods that are rich in iron, such as spinach, beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, and meat. Iron can help your body produce more red blood cells and prevent anemia, which can result from bleeding or low platelet count .
I hope this note helps you understand more about dengue fever, its cycle duration, pattern, preventive measures and treatment along with dietary support to treat this. Please take care and stay healthy.



Best one 👍☺️